What Are Nuclear Bombs? Safe Regulation Guide

Nuclear bombs, also known as atomic bombs, are a type of explosive device that derives its destructive power from nuclear reactions. These reactions involve the rapid release of energy from the nucleus of an atom, either through fission (splitting of heavy atoms) or fusion (combining of light atoms). The first nuclear bomb was developed during World War II as part of the Manhattan Project, a research and development project led by the United States with the participation of the United Kingdom and Canada. The devastating effects of nuclear bombs were first witnessed in August 1945, when atomic bombs were dropped on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leading to Japan's surrender and the end of World War II.
Understanding Nuclear Bombs

Nuclear bombs can be categorized based on their explosive mechanism into two main types: fission bombs and fusion bombs (also known as thermonuclear bombs). Fission bombs, like the ones dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, work by splitting heavy atomic nuclei (such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239) into lighter nuclei, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process. Fusion bombs, on the other hand, combine light nuclei (usually isotopes of hydrogen) into a heavier nucleus, also releasing a significant amount of energy. Fusion bombs are generally more powerful than fission bombs and are often used in hydrogen bombs.
Components of a Nuclear Bomb
A nuclear bomb consists of several critical components, including the fuel (fissionable material), a neutron initiator, reflectors, and a detonator. The fuel can be uranium-235 or plutonium-239 for fission bombs. The neutron initiator is used to start the chain reaction by releasing neutrons. Reflectors are used to surround the fuel and reflect neutrons back into the core, increasing the efficiency of the bomb. The detonator is a conventional explosive that compresses the fuel to achieve a supercritical mass, allowing the chain reaction to occur rapidly.
| Type of Nuclear Bomb | Description |
|---|---|
| Fission Bomb | Derives its power from the fission of heavy atomic nuclei. |
| Fusion Bomb (Thermonuclear Bomb) | Derives its power from the fusion of light atomic nuclei. |
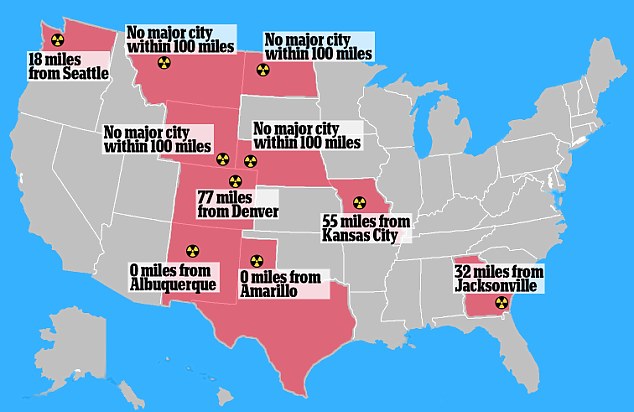
Safety and Regulation

The safety and regulation of nuclear bombs are of paramount importance due to their potential to cause catastrophic damage. International agreements, such as the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), aim to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, promote disarmament, and further the goals of nuclear non-proliferation and disarmament. The NPT, which came into force in 1970, is a cornerstone of international efforts to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and to promote cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
International Regulation Efforts
Besides the NPT, other key international regulations and initiatives include the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which bans all nuclear explosions, and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), which is responsible for verifying that nuclear energy is used for peaceful purposes. The IAEA conducts regular inspections of nuclear facilities and provides technical assistance to its member states to help them in applying nuclear technology for peaceful purposes, including electricity generation, medicine, and agriculture.
The regulation of nuclear bombs also involves strict national laws and international cooperation to prevent nuclear terrorism. The security of nuclear materials is a critical aspect of this regulation, as the diversion of such materials into the wrong hands could lead to the construction of improvised nuclear devices.
| International Agreement | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) | Prevents the spread of nuclear weapons and promotes disarmament and cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy. |
| Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) | Bans all nuclear explosions, whether for military or civilian purposes. |
Environmental and Health Impacts
The use of nuclear bombs has severe environmental and health impacts. The immediate effects include blast waves, thermal radiation, and ionizing radiation, which can cause widespread destruction and loss of life. Long-term effects include radioactive fallout, which can lead to cancer, genetic mutations, and other health problems. The environment is also severely affected, with radioactive materials contaminating soil, water, and air, leading to long-lasting ecological damage.
Examples of Environmental Damage
The Chernobyl nuclear disaster in 1986 and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 are examples of how nuclear accidents can have devastating environmental consequences. These incidents highlight the importance of safety measures, emergency preparedness, and international cooperation in the event of a nuclear accident.
In the context of nuclear bombs, the potential for environmental damage is exponentially higher due to the explosive nature of these devices. Therefore, preventing the use of nuclear bombs is crucial not only for humanitarian reasons but also for protecting the environment and ensuring the health and well-being of future generations.
| Nuclear Incident | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster | Large-scale radioactive contamination of the environment, affecting thousands of square kilometers. |
| Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster | Release of radioactive materials into the ocean and atmosphere, contaminating a significant area around the plant. |
What are the main types of nuclear bombs?
+
The main types of nuclear bombs are fission bombs, which work by splitting heavy atomic nuclei, and fusion bombs (thermonuclear bombs), which work by combining light nuclei.
What international agreements regulate nuclear weapons?
+
Key international agreements include the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), and the efforts of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to promote the safe and peaceful use of nuclear energy.
What are the environmental and health impacts of nuclear bombs?
+
The use of nuclear bombs can lead to immediate and long-term health effects, including radiation sickness, cancer, and genetic mutations, as well as severe environmental damage through radioactive fallout, contaminating soil, water, and air.